Coagulation Practice Questions
Looking to sharpen your skills in coagulation for the ASCP Medical Laboratory Scientist (MLS) exam? Whether you’re just starting your review or aiming to master the final stretch, focusing on coagulation is a must. This crucial subject encompasses everything from the intricacies of clotting factor pathways to the interpretation of coagulation studies, including PT, aPTT, and mixing studies. The carefully selected 25 Coagulation Practice Questions for ASCP are tailored to help you grasp both foundational and advanced topics. Each question is carefully crafted to reflect the ASCP exam style, providing you with a practical and focused way to prepare.
These 25 Coagulation Practice Questions will guide you through high-yield content such as factor deficiencies, anticoagulant monitoring, and fibrinolytic mechanisms. After each question, you’ll find clear and concise explanations that not only provide the correct answer but also help reinforce the underlying concepts. So, let’s dive in and boost your confidence, one question at a time!
🟢 Easy Questions
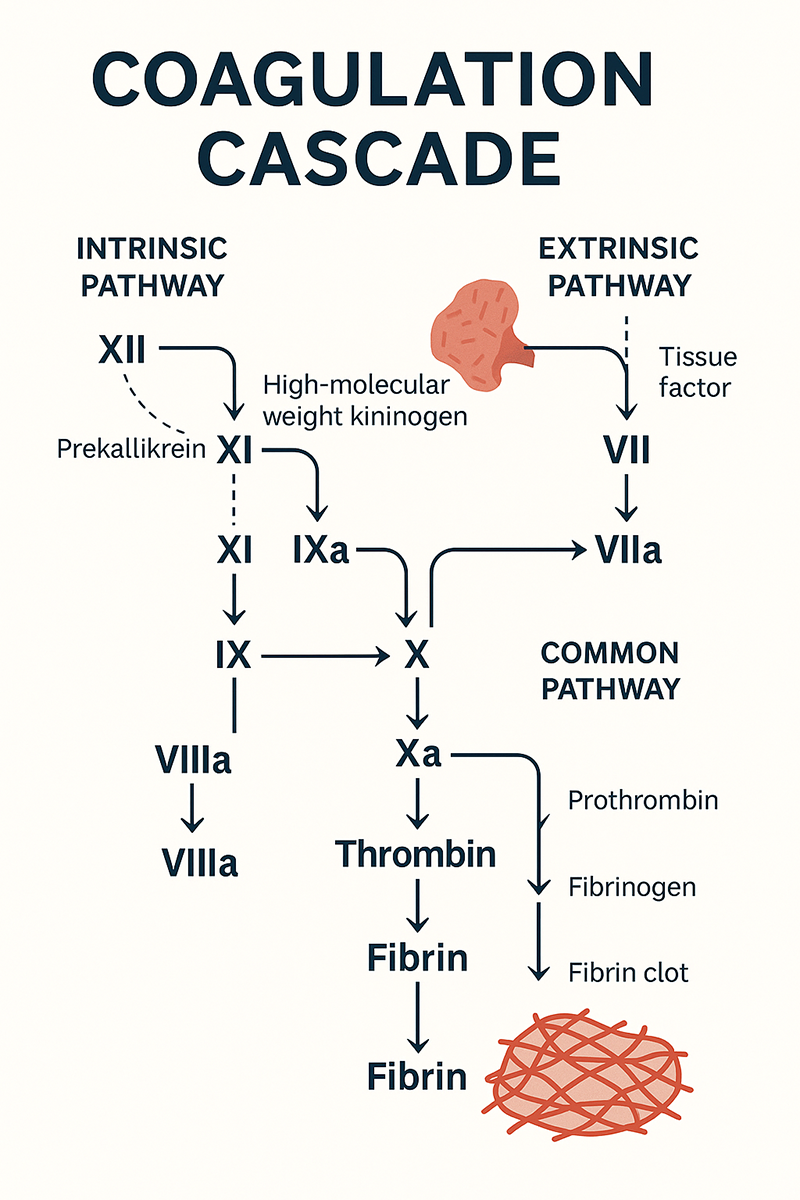
1. When evaluating the coagulation system, which pathway does the Prothrombin Time (PT) specifically measure?
A. Intrinsic pathway
B. Extrinsic pathway
C. Common pathway
D. Fibrinolytic pathway
✅ Answer: B. Extrinsic pathway
🧠 Explanation:
PT assesses the extrinsic and common pathways, specifically factors I, II, V, VII, and X.
2. Which factor is also known as fibrinogen?
A. Factor I
B. Factor II
C. Factor III
D. Factor IV
✅ Answer: A. Factor I
🧠 Explanation:
Factor I is fibrinogen, a soluble protein converted to fibrin during clot formation.
3. Among essential nutrients, which vitamin plays a key role in synthesizing Factors II, VII, IX, and X?
A. Vitamin A
B. Vitamin D
C. Vitamin K
D. Vitamin C
✅ Answer: C. Vitamin K
🧠 Explanation:
Vitamin K is critical for gamma-carboxylation of several clotting factors, enabling calcium binding.
4. As the coagulation process advances, what crucial role does thrombin play in the cascade?
A. Dissolves clots
B. Converts fibrinogen to fibrin
C. Activates Vitamin K
D. Inhibits platelets
✅ Answer: B. Converts fibrinogen to fibrin
🧠 Explanation: Thrombin plays a central role by converting fibrinogen into fibrin, forming the final clot matrix.
5. The Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (aPTT) evaluates:
A. Extrinsic and common pathways
B. Only the extrinsic pathway
C. Only the intrinsic pathway
D. Intrinsic and common pathways
✅ Answer: D
🧠 Explanation:
aPTT measures the function of the intrinsic and common pathways, including factors VIII, IX, XI, and XII.
🟡 Medium Questions
6. A prolonged PT with a normal aPTT suggests a deficiency in:
A. Factor VIII
B. Factor IX
C. Factor VII
D. Factor X
✅ Answer: C
🧠 Explanation:
Factor VII is unique to the extrinsic pathway; its deficiency prolongs PT but not aPTT.
7. Which of the following is a natural anticoagulant?
A. Factor V
B. Thrombin
C. Protein C
D. von Willebrand Factor
✅ Answer: C
🧠 Explanation:
Protein C, once activated, inhibits Factors Va and VIIIa, regulating clot formation.
8. When managing patients on anticoagulant therapy, which coagulation test is most commonly used to monitor unfractionated heparin treatment?
A. PT
B. aPTT
C. TT
D. INR
✅ Answer: B
🧠 Explanation:
aPTT is prolonged with heparin therapy, making it the appropriate monitoring test.
9. What is the primary role of calcium (Factor IV) in coagulation?
A. Fibrinolysis
B. Platelet destruction
C. Enzyme inhibition
D. Activation of several clotting factors
✅ Answer: D
🧠 Explanation:
Calcium acts as a cofactor for activating multiple clotting factors, supporting cascade progression.
10. A deficiency in which factor causes Hemophilia B?
A. Factor VIII
B. Factor IX
C. Factor XI
D. Factor V
✅ Answer: B
🧠 Explanation:
Hemophilia B, also known as Christmas disease, results from a Factor IX deficiency.
11. In performing the Prothrombin Time (PT) test, which reagent is essential for initiating the extrinsic pathway of coagulation?
A. Calcium and thromboplastin
B. Calcium and kaolin
C. Platelet-poor plasma
D. Buffer and saline
✅ Answer: A
🧠 Explanation:
PT testing involves adding tissue thromboplastin and calcium to plasma to trigger the extrinsic pathway.
12. The INR (International Normalized Ratio) standardizes which test?
A. TT
B. aPTT
C. PT
D. Bleeding time
✅ Answer: C
🧠 Explanation:
INR standardizes PT results across labs to monitor warfarin therapy effectively.
13. In the context of clot formation, which clotting factor is stabilized and carried by von Willebrand Factor in circulation?
A. Factor II
B. Factor IX
C. Factor VII
D. Factor VIII
✅ Answer: D
🧠 Explanation:
vWF binds and protects Factor VIII from degradation in circulation.
14. A patient with a normal PT but prolonged aPTT may have:
A. Factor VII deficiency
B. Factor X deficiency
C. Factor IX deficiency
D. Liver disease
✅ Answer: C
🧠 Explanation:
Only the intrinsic pathway is affected in Factor IX deficiency, prolonging aPTT without affecting PT.
15. When screening for lupus anticoagulant, which coagulation test is most significantly affected by its presence?
A. Bleeding time
B. PT
C. aPTT
D. Fibrinogen
✅ Answer: C
🧠 Explanation:
Despite its name, lupus anticoagulant prolongs aPTT in vitro, though it promotes thrombosis in vivo.
🔴 Hard Questions
16. When studying the intrinsic pathway of coagulation, which clotting factor is commonly referred to as Hageman factor?
A. Factor XII
B. Factor XI
C. Factor X
D. Factor IX
✅ Answer: A
🧠 Explanation:
Factor XII is also called Hageman factor and initiates the intrinsic pathway in vitro.
17. What condition is characterized by simultaneous thrombosis and bleeding due to consumption of clotting factors?
A. Hemophilia
B. DIC
C. Von Willebrand Disease
D. Thrombocytopenia
✅ Answer: B
🧠 Explanation:
In Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC), widespread clotting depletes factors, causing bleeding.
18. Reptilase time differs from thrombin time in that:
A. It’s shorter
B. It’s unaffected by heparin
C. It needs calcium
D. It’s used for PT measurement
✅ Answer: B
🧠 Explanation:
Reptilase time is similar to thrombin time but unaffected by heparin, helping in heparinized samples.
19. Factor XIII deficiency affects clotting by:
A. Inhibiting thrombin
B. Delaying platelet aggregation
C. Preventing fibrin cross-linking
D. Accelerating fibrinogen cleavage
✅ Answer: C
🧠 Explanation:
Factor XIII stabilizes the clot by cross-linking fibrin strands. Without it, clots are unstable.
20. In hereditary bleeding disorders, which inherited condition is known to cause prolonged results in both PT and aPTT tests?
A. Hemophilia A
B. Factor VII deficiency
C. Factor X deficiency
D. vWD
✅ Answer: C
🧠 Explanation:
Factor X is part of the common pathway; its deficiency prolongs both PT and aPTT.
21. What is the significance of D-dimer testing?
A. Rule out thrombosis
B. Assess fibrinogen
C. Monitor warfarin
D. Confirm Factor VIII activity
✅ Answer: A
🧠 Explanation:
Elevated D-dimer levels indicate fibrin breakdown and help rule out thrombosis or DIC.
22. When evaluating a patient with bleeding symptoms, which condition typically presents with a prolonged bleeding time while both PT and aPTT remain within normal limits?
A. Hemophilia A
B. Von Willebrand Disease
C. Liver cirrhosis
D. DIC
✅ Answer: B
🧠 Explanation:
vWD affects platelet adhesion, causing prolonged bleeding time while clotting times may appear normal.
23. During the evaluation of abnormal coagulation results, which laboratory test is used to distinguish between a clotting factor deficiency and the presence of an inhibitor?
A. PT
B. Mixing study
C. INR
D. TT
✅ Answer: B
🧠 Explanation:
A mixing study adds normal plasma; correction suggests deficiency, while no correction suggests inhibitor.
24. In clinical settings involving abnormal clot breakdown, which condition is most commonly associated with elevated fibrin degradation products (FDPs)?
A. Hemophilia
B. DIC
C. vWD
D. Heparin overdose
✅ Answer: B
🧠 Explanation:
In DIC, excessive clot formation and breakdown elevate FDPs, including D-dimer.
25. The initial step in coagulation after vessel injury is:
A. Platelet aggregation
B. Thrombin activation
C. Vasoconstriction
D. Tissue factor release
✅ Answer: C
🧠 Explanation:
Vasoconstriction occurs first to minimize blood loss, followed by platelet adhesion and coagulation.
RESOURCES :
Rodak BF, Fritsma GA, Keohane EM. Hematology: Clinical Principles and Applications, 5th ed.
ASCP BOC Study Guide for Clinical Laboratory Certification Exams
Clinical Hematology and Fundamentals of Hemostasis – Harmening
- https://www.uptodate.com/
- https://www.medscape.com/
